Nulands Limited transforms land into thriving communities, offering secure and affordable property solutions across Kenya.
Your search results
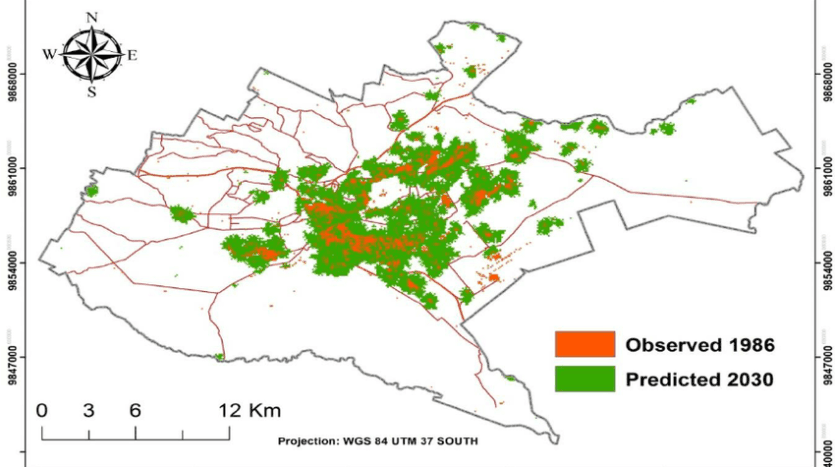
Kenya’s Urban Sprawl and its Influence on Sustainable Housing Development
The rapid rate of urbanization in cities and towns across Kenya have taken on different forms since the start of rural to urban migration in the post-colonial era. One such form of urbanization is called urban sprawl or urban encroachment. What effects do they have in urban planning and sustainable housing development in Kenya and what can be done to face the challenges?
By definition, urban sprawl is the rapid expansion of the geographic boundaries of cities and towns. Or the spreading of urban infrastructure on undeveloped areas near a city or a town.
Urban sprawl is characterized by:
- low-density residential housing,
- single-use zoning (such as houses only, or apartment buildings only, or office buildings only), and
- increased reliance on private transportation due to distance from designated infrastructure like highways.
Understanding Urban Sprawl
Urban sprawl is the effect of unplanned growth where urban migration spread into previously undeveloped land, such as designated agricultural land and wetland at the outskirts of urban areas. The result is encroachment of communities into low-or high-density areas, isolated from county, city, or town urban planning strategies in the form of infrastructure and amenities such as schools, tarmacked roads and highways, and public service offices.
In Kenya, urban sprawl is caused by factors that include:
- Population growth – when the rate of rural to urban migration increases, and demand for housing is higher than the supply, and prices for rent, good and services increase, there are segments of the population that opt for urban sprawl.
- Pursuit of economic opportunities – when a new factory, plant, or mega project emerges at the outskirts of the city, staff will want to live in close proximity to avoid spending long hours commuting to work and also to save on transport costs. Families will move into an urban sprawl in order to take advantage of the job opportunities.
- The desire for spacious living – Some families will prefer to move out of congested and densely populated urban areas for a chance to live in an urban sprawl for reasons such as fresh air.
Urban sprawl is known to overtake urban development, which relies on urban planning and in the process affect housing development in several ways:
The Effects of Urban Sprawl on Housing Development
- Land Consumption and Environmental Degradation: Agricultural land use is the first casualty of urban sprawl that leads to encroachment on agricultural areas, forests, and wetlands. This affects the availability of land for food production and biodiversity, and promotes environmental degradation. Green spaces and ecosystems also fall victim as part of environmental damage which leads to the effects of climate change like floods, landslides, heatwaves, loss of lives, and reduced quality of life for urban area residents.
- Infrastructure Strain: Urban encroachment places a strain on the infrastructure. Extending connections for water, sewer, electricity, and public transport networks, and services like police, fire fighters, and health to sprawling suburbs can be costly especially when delayed.
Low-income communities can suffer because of risks associated with lack of basic services like tap water, legal electricity connection, and access roads. This can be catastrophic in case of an emergency like a fire or floods and can lead to tragic losses due to the delays in accessing the location of the incident.
- High Transport Costs: Urban sprawl that emerge a great distance from the main roads will also mean a longer commute to and from places of work, education centers, and recreation facilities for the community. This will increase dependence on public means of transport like “bodabodas” for middle and low-income areas and more cost on fuel for all long-distance movements. High transport costs will also be a strain on household expenses, a security risk for late night workers, and extended hours for the average family.
- Affordable Housing: Unchecked expansion of the urban sprawl can increase the demand for land and housing and this can challenge the possibility of constructing affordable housing in the community. Land speculation, land cartels, and the lack of coordinated urban planning can lead to inflated property values and push out low-income residents to further isolated areas or back to the informal settlements.
The Role of Sustainable Housing
The vision of sustainable housing is included in the UN General Assembly’s Sustainable Development Goals no.11 regarding sustainable cities and communities. It is also a key pillar in both the Big 4 Agenda and the current government’s Bottom-up Economic Transformation Agenda (BETA) manifesto. There is a global and national effort in place to develop sustainable housing that meets the needs of communities while minimizing environmental impact and promoting equity. Urban sprawl can promote sustainable urban development through a number of strategies:
- Smart Growth: Smart growth uses compact, mixed-use development to promote high density living and reduce the footprint of urban areas. Mixed-use developments merge residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, to promote livability and reduce several inconveniences. For example, by constructing retail shops within residential buildings to reduce the time and distance used to purchase fast-moving consumer goods. Another example is efficient use of land and resources within cities to reduce the negative impacts of urban sprawl.
- Transportation and Movement: Well-run public transport vehicles and promoting non-motorized means of transport such as cycling can lessen the transportation challenges associated with urban sprawl. Walking and cycling tracks in the housing areas can increase accessibility and promotes healthy living.
- Building Green: Green building practices can reduce environmental impact, enhance energy efficiency, and promote overall sustainable housing. This includes using eco-friendly building materials, energy-efficient designs, and renewable energy sources such as solar power. Building green is affordable, reduces the environmental footprint, and lower utility costs for residents.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Strong housing policies are key for an effective urban planning and sustainable housing development framework. The government of Kenya has the mandate to implement policies that promote smart housing, building green techniques, and affordable housing development which can all reduce the negative effects of urban sprawl.
How Urban Planning Tackles Urban Sprawl
In Kenya, urban planning is the antidote of the challenges posed by urban sprawl. The core responsibility for urban planning is to promote sustainable housing development. Urban planning needs government involvement in facilitating land usage and distribution, setting transportation infrastructure, and being involved in affordable housing and design development to create a cohesive urban environment. Additionally, the government can promote urban planning and tackle urban sprawl by:
- Consultative Planning: Urban planning needs to consider the input of professionals from the public and private sector to ensure that housing development aligns with infrastructure goals, transport network blueprints, and environmental conservation.
- Public Participation: Engaging communities in the planning process promotes acceptance by the residents as they feel heard by the government. It also ensures that the success of the housing projects means to meet the needs and priorities of residents. Community-led housing initiatives such as self-build houses use public engagements to empower residents and promote social cohesion.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Monitoring and evaluation of urban development is a phase to assess impact and effectiveness and reduce future occurrence. M&E also identifies the challenges of the community and implement corrective measures. The results include the alignment of urban planning with sustainable development.
Urban sprawl hinders urban planning and sustainable housing development in Kenya. Sustainable urban planning practices prioritize mixed-use development, efficient transport systems, building green, and strong housing policies. Likewise, sustainable development can boost inclusive, resilient, and eco-friendly cities and towns, and ensure a high quality of life for many citizens. Urban planning for sustainable cities can promote economic development and reduce the effects of urban sprawl through social equity and environmental stewardship.